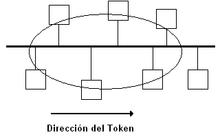
Token bus is a network implementing a Token Ring protocol over a virtual ring on a coaxial cable.[1] A token is passed around the network nodes and only the node possessing the token may transmit. If a node doesn't have anything to send, the token is passed on to the next node on the virtual ring. Each node must know the address of its neighbour in the ring, so a special protocol is needed to notify the other nodes of connections to, and disconnections from, the ring.[2]
Due to difficulties handling device failures and adding new stations to a network, Token Ring gained a reputation for being unreliable and difficult to upgrade. Bus networks, such as Ethernet, had a more flexible and reliable physical architecture, but Ethernet's access protocol could not absolutely guarantee a maximum time any station would have to wait to access the network, so was thought to be unsuitable for manufacturing automation applications. The Token bus protocol was created to combine the benefits of a physical bus network with the deterministic access protocol of a Token Ring network.[3]
Token bus was standardized by IEEE standard 802.4. It was mainly used for industrial applications. Token bus was used by General Motors for their Manufacturing Automation Protocol (MAP) standardization effort.[4] This is an application of the concepts used in Token Ring networks. The main difference is that the endpoints of the bus do not meet to form a physical ring.
In order to guarantee the packet delay and transmission in Token bus protocol, a modified Token bus was proposed in Manufacturing Automation Systems and flexible manufacturing system (FMS).
A means for carrying Internet Protocol over IEEE 802 networks, including token bus networks, was developed.[5]
The IEEE 802.4 Working Group has disbanded and the standard has been withdrawn by the IEEE.[6]
See also
References
- ^ "Token Bus Network". Retrieved 2012-03-21.
- ^ "Token Bus (IEEE 802.4)". Retrieved 2012-03-21.
- ^ "Token Bus and Token Ring". Retrieved 2012-03-21.
- ^ Weaver, A.C.; Summers, C.F. (February 1988). "The IEEE token bus-A performance bound on GM MAP". Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on. 35: 13–17. doi:10.1109/41.3057.
- ^ RFC 1042
- ^ "IEEE 802 Working Group & Executive Committee Study Group Home Pages". IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee. Retrieved 2012-03-21.