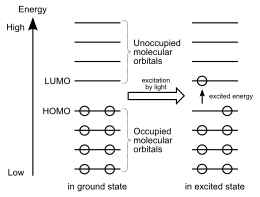
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, respectively.
HOMO–LUMO gap
The energy difference between the HOMO and LUMO is termed the HOMO–LUMO gap. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the frontier orbitals, such as in the frontier molecular orbital theory. The difference in energy between these two frontier orbitals can be used to predict the strength and stability of transition metal complexes, as well as the colors they produce in solution.[1]
Semiconductors
The HOMO level to organic semiconductors is roughly what the maximum valence band is to inorganic semiconductors and quantum dots. The same analogy can be made between the LUMO level and the conduction band minimum.[2]
Organometallic chemistry
In organometallic chemistry, the size of the LUMO lobe can help predict where addition to pi ligands will occur.
SOMO
A SOMO is a singly occupied molecular orbital such as half-filled HOMO of a radical.[3] This abbreviation may also be extended to semi occupied molecular orbital.
Subadjacent orbitals: NHOMO and SLUMO
If existent, the molecular orbitals at one energy level below the HOMO and one energy level above the LUMO are also found to play a role in frontier molecular orbital theory. They are named NHOMO for next-to-highest occupied molecular orbital and SLUMO for second lowest unoccupied molecular orbital.[4] These are also commonly referred to as HOMO-1 and LUMO+1, respectively.
See also
- Diels–Alder reaction
- Electron configuration
- Klopman-Salem equation
- Koopmans' theorem
- Ligand
- Organic semiconductor
References
- ^ Griffith, J.S. and L.E. Orgel. "Ligand Field Theory". Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1957, 11, 381-383
- ^ Bredas, J,-L. "Mind the gap!". Mater. Horiz. 2014,1, 17-19
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "SOMO". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S05765
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "subjacent orbital". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S06067
External links
- OrbiMol Molecular orbital database