| General visceral efferent fibers | |
|---|---|
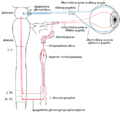
 Scheme showing structure of a typical spinal nerve. 1. Somatic efferent. 2. Somatic afferent. 3,4,5. Sympathetic efferent. 6,7. Sympathetic afferent. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
The term general efferent fibers (GVE or visceral efferent or autonomic efferent) refers to the efferent neurons of the autonomic nervous system that provide motor innervation to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands (contrast with SVE fibers) through postganglionic varicosities.[1]
GVE fibers may be either sympathetic or parasympathetic.[2]
The cranial nerves containing GVE fibers include the oculomotor nerve (CN III), the facial nerve (CN VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and the vagus nerve (CN X).[3]
Additional images
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 849 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)