 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
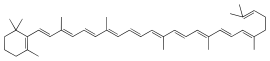
| IUPAC name β,ψ-Carotene | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 2-((1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E,19E)-3,7,12,16,20,24-hexamethylpentacosa-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,23-undecaen-1-yl)-1,3,3-trimethylcyclohex-1-ene | |
| Other names β,psi-Carotene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C40H56 |
| Molar mass | 536.888 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 160 to 162 °C (320 to 324 °F; 433 to 435 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
γ-Carotene is a carotenoid, and is a biosynthetic intermediate for cyclized carotenoid synthesis in plants. It is formed from cyclization of lycopene by lycopene cyclase epsilon.[2] Along with several other carotenoids, γ-Carotene is a vitamer of vitamin A in herbivores and omnivores. Carotenoids with a cyclized, beta-ionone ring can be converted to vitamin A, also known as retinol, by the enzyme Beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase; however, the bioconversion of gamma-carotene to retinol has not been well-characterized.
References
- ^ Ruegg, R.; Schwieter, U.; Ryser, G.; Schudel, P.; Isler, O. (1961). "Synthesen in der Carotinoid-Reihe. 17. Mittelung. γ-Carotin sowie d,l-α- und β-Carotin aus Dehydro-β-apo-12′-carotinal(C25)". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 44 (4): 985–93. doi:10.1002/hlca.19610440414.
- ^ Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Stange C. Biosynthesis of carotenoids in carrot: an underground story comes to light. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 2013;539:110-6.