 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
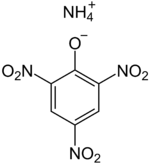
| IUPAC name Ammonium 2,4,6-trinitrophenolate | |
| Other names Ammonium picrate; Picratol; 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol ammonium salt; Ammonium picronitrate; Explosive D | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.582 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C6H6N4O7 |
| Molar mass | 246.135 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.719 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 265 °C (509 °F; 538 K)[1] |
| 10 g/L (20 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R3 R23/24/25 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2) S28 S35 S37 S45 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Dunnite, also known as Explosive D or systematically as ammonium picrate, is an explosive developed in 1906 by US Army Major Beverly W. Dunn, who later served as the chief inspector of the Bureau of Transportation Explosives.[2][3] Ammonium picrate is a salt formed by reacting picric acid and ammonia. It is chemically related to the more stable explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT).
History
It was the first explosive used in an aerial bombing operation in military history, performed by Italian pilots in Libya in 1911.[4] It was used extensively by the United States Navy during World War I.[5]
Though Dunnite was generally considered an insensitive substance, by 1911 the United States Army had abandoned its use in favor of other alternatives.[6] The Navy, however, used it in armor-piercing artillery shells and projectiles, and in coastal defense.
Dunnite typically did not detonate on striking heavy armor. Rather, the shell encasing it would penetrate the armor, after which the charge would be triggered by a base fuze.
In 2008 caches of discarded Dunnite in remote locations were mistaken for rusty rocks at Cape Porcupine, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada.[7][8]
Dunnite can be used as a precursor to the highly stable explosive TATB (1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene), by first dehydrating it to form picramide (attaching the ammonia as an amine group instead of an ion) and then further aminating it.
References
- ^ a b Record of Ammoniumpikrat in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 24. Nov. 2007.
- ^ War Records Committee of the Alumni Association (1920), Technology's War Record: An Interpretation of the Contribution Made by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, its Staff, its Former Students and its Undergraduates to the Cause of the United States and the Allied Powers in the Great War, 1914-1919, Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, p. 364
- ^ Dunnite Smashes Strongest Armor, The New York Times, August 18, 1907
- ^ [1], La Stampa, November 2, 1911
- ^ Dunnite, Firstworldwar.com
- ^ Ridicule Spy Story: Army Abandoned the Use of Dunnite Years Ago, Officers Say, The New York Times, August 8, 1911
- ^ Family makes explosive discovery on Labrador shore, The Globe and Mail, Toronto, Ontario, September 11, 2008.
- ^ "Beachcombing Labrador family carries home wartime explosive". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. 2008-09-10. Retrieved 2017-01-07.