| Common palmar digital nerves of median nerve | |
|---|---|
 Superficial palmar nerves. | |
 Deep palmar nerves. | |
| Details | |
| From | median nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervi digitales palmares communes nervi mediani |
| TA98 | A14.2.03.038 |
| TA2 | 6465 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
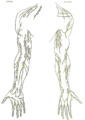
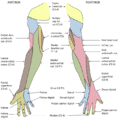
In the palm of the hand the median nerve is covered by the skin and the palmar aponeurosis, and rests on the tendons of the Flexor muscles. Immediately after emerging from under the transverse carpal ligament the median nerve becomes enlarged and flattened and splits into a smaller, lateral, and a larger, medial portion.
The medial portion of the nerve divides into two Common palmar digital nerves (common volar digital nerves).
- The first of these gives a twig to the second Lumbricalis and runs toward the cleft between the index and middle fingers, where it divides into two proper digital nerves for the adjoining sides of these digits;
- the second runs toward the cleft between the middle and ring fingers, and splits into two proper digital nerves for the adjoining sides of these digits; it communicates with a branch from the ulnar nerve and sometimes sends a twig to the third Lumbricalis.
Additional images
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 938 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson5nervesofhand at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)